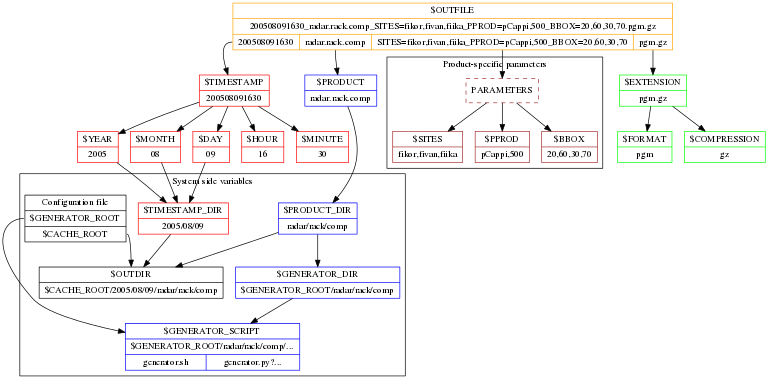
NutShell Variables¶
System variables¶
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
PRODUCT |
Product id, eg. | “my.test.product” |
TIMESTAMP |
Numeric time or “LATEST”<br> or “LATEST” or “TIMESTAMP” | “201708121600” |
-- YEAR |
Year (4 digits) | “2017” |
– MONTH |
Month (2 digits) | “08” |
– DAY |
Day (2 digits) | “12” |
– HOUR |
Hour (2 digits) | “16” |
– MINUTE |
Minute (2 digits) | “00” |
PARAMETERS |
Product specific variables | {“SIZE”: “300”, “NAME”: “X”} |
– <KEY> |
Name of a variable | “300” |
– <KEY> |
Name of a variable | “X” |
| – … | … | … |
EXTENSION |
File format, including compression | “txt.gz” |
FORMAT |
File format | “txt” |
COMPRESSION |
File compression | “gz” |
In code, nutshell.product.Info provides parsing of above parameters.
Part of the variables come from Configuration files read by nutshell.nutshell.ProductServer .
Variable parsing scheme¶
Parsing can be tested interactively:
>>> import nutshell.product
>>> p = nutshell.product.Info("201708121600_my.test.product_SIZE=300.pgm.gz")